Autonomous Mobile Robot for Warehous Industries
Developed an AMR prototype with autonomous navigation in indoor environments.
This project demonstrates the design and implementation of an Omni-Wheeled Autonomous Mobile Robot (AMR) tailored for automating repetitive and time-intensive warehouse operations. The solution integrates cutting-edge robotics, SLAM technologies, and efficient hardware to embody the principles of Industry 4.0.
Hardware and Mechanical Design
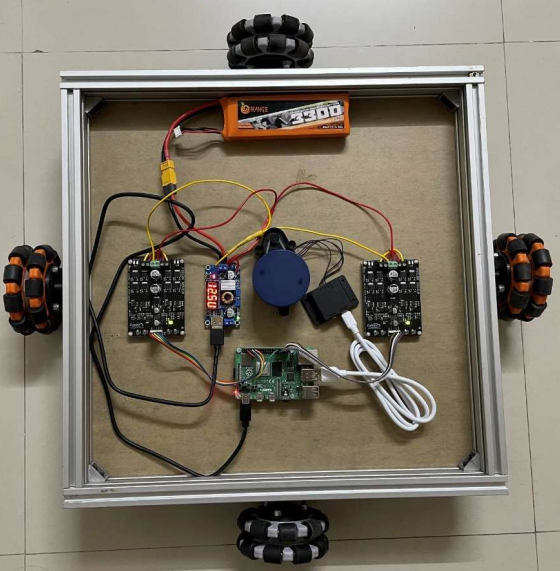
Components Utilized:
- Raspberry Pi 4B: Acts as the central processing unit for controlling navigation and decision-making.
- 360 degree LiDAR Sensor: Facilitates environment scanning for mapping and obstacle detection, ensuring efficient path planning.
- Omni-Wheels: Provide multidirectional mobility, enabling the robot to maneuver smoothly in tight and dynamic warehouse environments.
- Motor Drivers: Control wheel movement, translating navigation commands into precise actions.
- Power System: A 2200mAh Li-ion battery ensures sustained operation, stabilized by power regulators for consistent performance.
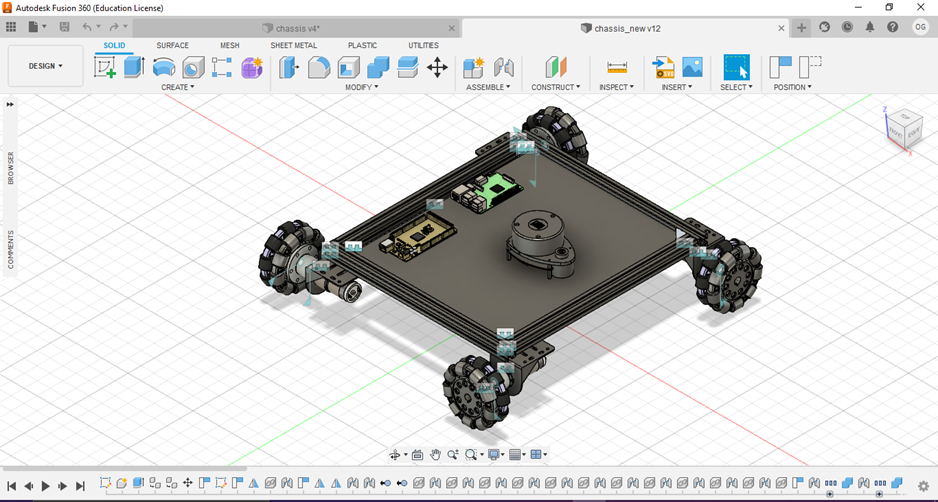
Mechanical Construction:
- The robot was designed with a focus on structural durability and modularity, simplifying maintenance and component replacement.
- Integration of URDF models and 3D drawings allowed for simulation testing of robot movement and behavior prior to physical deployment.
Software Integration
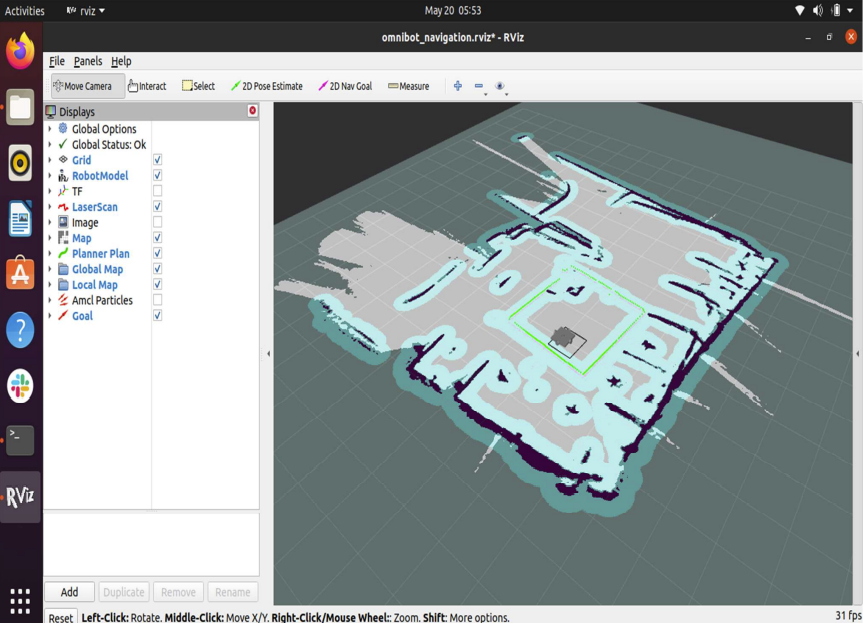
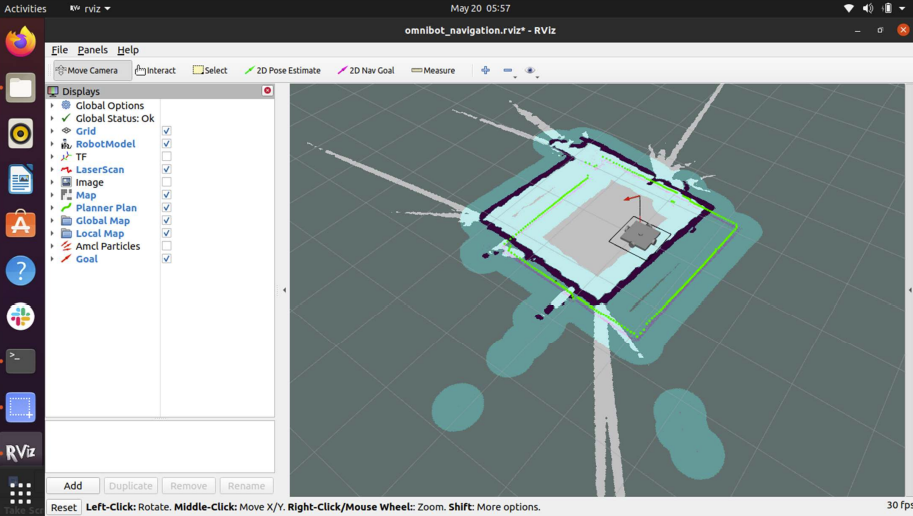
Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM):
- SLAM algorithms enable the robot to construct detailed indoor maps and localize itself within the environment. This is critical for real-time path planning and navigation.
- The LiDAR sensor provides high-resolution environmental data for precise mapping.
Caption photos easily. On the left, a road goes through a tunnel. Middle, leaves artistically fall in a hipster photoshoot. Right, in another hipster photoshoot, a lumberjack grasps a handful of pine needles.
This image can also have a caption. It's like magic.
Path Planning and Navigation:
- Real-time pathfinding algorithms guide the robot efficiently between locations, avoiding static and dynamic obstacles.
- Integrated control systems ensure smooth transitions and accurate alignment during operations. Interfacing and Communication:
Potential Applications
- Warehousing: Automating goods movement and inventory management.
- Manufacturing: Streamlining material handling between production stages.
- Healthcare: Transporting medical supplies in large facilities.
This project highlights the transformative potential of robotics in industry, particularly for small-scale businesses looking to embrace automation.